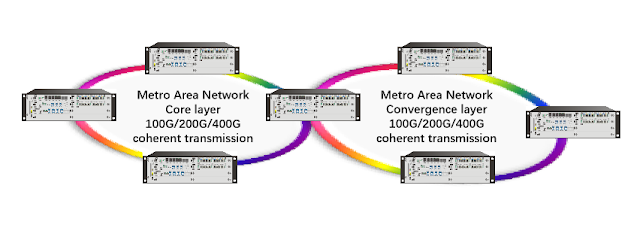
DWDM/OTN Application Scenario
WDM technology has many advantages and is developing rapidly. Main features include: 1) The bandwidth resources of the optical fiber can be used to increase the transmission capacity of an optical fiber several times to several tens of times compared with single-wavelength transmission; 2) multi-wavelength multiplexing in single-mode optical fiber transmission can save a lot of optical fiber during large-capacity long-distance transmission; 3) The installed cable has a small number of cores, and the wavelength division multiplexing can be used to expand the capacity without major changes to the original system; 4) since the wavelengths of the signals transmitted in the same fiber are independent of each other, signals with completely different characteristics can be transmitted. 5) T he wavelength division multiplexing channel is transparent to the data format, that is, it has nothing to do with the signal rate and electrical modulation mode. 6) A WDM system can carry multiple fo...



